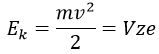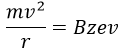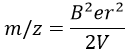La spectrométrie de masse est l’une des techniques les plus utilisées dans les laboratoires car elle permet de déterminer la structure d’une molécule. Pour cette technique, l’échantillon doit être une solution pure, contenant une seule molécule qui sera analysée dans un délai très court. C’est pourquoi les spectromètres de masse font souvent la queue sur une colonne chromatographique (HPLC ou GC). La solution quittant la colonne est séparée en petits échantillons qui sont directement analysés dans le spectromètre de masse.
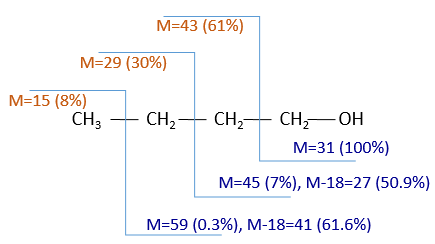
Le principe est assez simple: nous détruisons la molécule par un bombardement d’électrons ou de cations et nous détectons ses bits, les ions gazeux.
Les clivages des molécules ne sont pas totalement aléatoires et obéissent à quelques règles. Il en résulte des ions caractéristiques dont la nature peut être directement déterminée. La détection des ions se fait en fonction de leur rapport masse/charge m/z (et donc de leur masse). La masse des ions est l’addition de la masse des atomes qui les composent. Notez que la masse écrite sur la table de Mendeleev (la masse chimique) n’est pas la masse d’un atome mais l’addition pondérée des masses de ses isotopes. L’utilisation des masses chimiques est pertinente dans le cas des solutions macroscopiques, mais dans le cas de la spectrométrie de masse, nous détectons chaque ion unique de sorte que les masses atomiques doivent être utilisées. Le fait que différents isotopes d’un seul atome soit dans l’échantillon peut même nous donner des conseils sur la nature des espèces ioniques. Pour déterminer quelle molécule se trouvait dans l’échantillon, nous nous trouvons ensemble. Il ya quelques programmes qui peuvent faire le déroutant par lui-même.
Le spectromètre de masse :
Le principe d’un spectromètre de masse est de dévier ou d’accélérer des ions à partir ou vers un détecteur en fonction de leurs masses. Plusieurs modèles de MS existent et ce n’est pas le but du cours de les décrire tous, mais il est encore important de comprendre comment fonctionne le SM. Un spectromètre est toujours composé de quelques compartiments caractéristiques:
Une chambre d’ionisation
Un séparateur / analyseur
Un détecteur
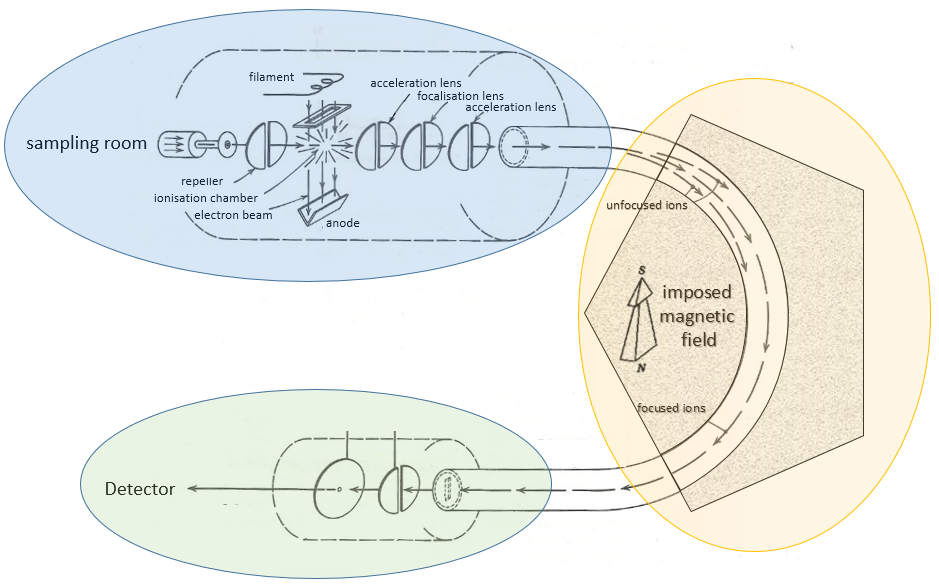
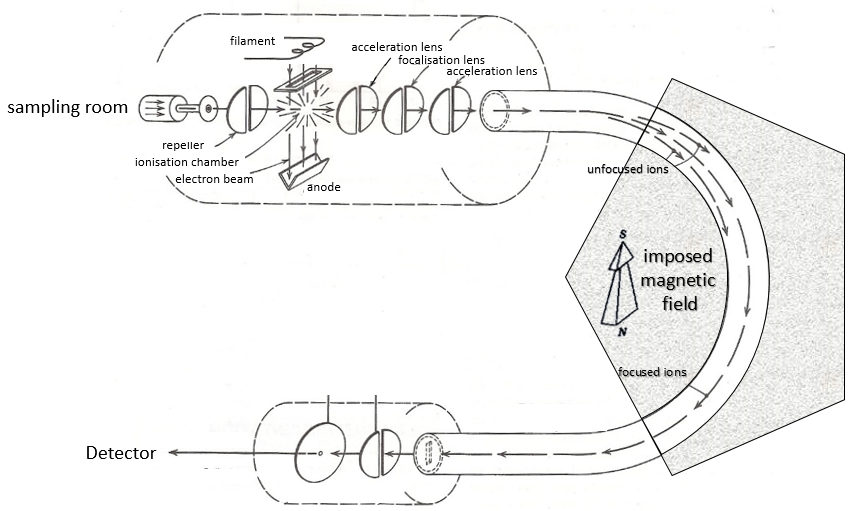
Voici un schéma d’un spectromètre de masse à déflexion magnétique.
We will describe briefly each part.
Sampling
The first step of the analysis is to ionise the sample. It is done in an ionisation chamber. There are three ways to introduce a sample in this chamber:
- direct introduction system: the sample is placed in a capillary that is set in the ionisation chamber. In this chamber, the pressure is extremely low (≈10-5 torr): the void is expected to avoid any recombination between the ions. The difference of pressure will transport the sample to where it will be ionised. This method is used for samples that are not volatile.
- reservoir system: the sample is injected in a reservoir oven heated at a given temperature. The samples that are volatile become gaseous and are transported towards the ionisation chamber by a difference of pressure. The pressure in the reservoir is set to 10-2 torr versus 10-5 torr in the chamber.
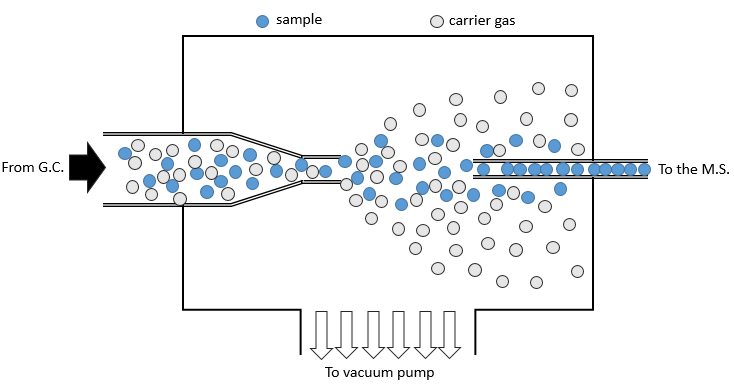
- from chromatography: a gaseous sample comes directly from a GC (gaseous chromatography). Before the introduction in the ionisation chamber, we separate the substrate from the carrier gas . The mass of carrier gas is in general way smaller than the mass of the substrate. We can use this difference to separate them: a thin tube is in front of the exit of the GC. A pump is placed perpendicularly to pump out the gas. As the carrier gas is lighter than the substrate, it is more deviated and does not reach the exit tube. The sample is thus purified.
Ionisation
The goal of the ionisation is to form positively charged ions from the substrate. To do so, the sample is bombarded (by electrons or by cations) to expulse more electrons from the molecules.
The typical range of energy that is required for the ionisation is 8 to 15 eV. As we want to be sure that the substrate is ionised, we inject more energy than required (50-70eV). It is possible to get a double ionisation. The excess of energy can break the ion into smaller ions.
This process can be repeated several times and from one substrate we can have dozens of fragments.
There are two methods of ionisation:
- electronic bombardment
A beam of electrons comes from a heated metal such as a tungsten filament. The electrons collide perpendicularly with the substrate to produce the ionised species that are directed towards the detector by a repeller. The neutral molecules (not ionised or resulting from subsequent cleavages) are removed through a pump
- chemical bombardment
This method is sweeter than the electronic bombardment. It leads to less fragmentation. The energy of ionisation is given by the collision with cations that eventually give a proton to the substrate, increasing its mass by one unit (it is important for later).
Analyser
The difference between different models of mass spectrometers essentially lies in the separation method they are equipped with.
The ionised species are not directly sent to the detector. Before that they have to pass through an analyser. Its role is whether to block some of the species before the detector or to separate them on their way.
Flying time
As simple as it sounds: the ionised molecules are accelerated straight towards the detector without any deflection. The time between the ionisation and the detection is measured. This time is characteristic of the mass of the molecule (t∼√M): small molecules make the distance in a shorter time than large molecules.
Magnetic deflection
On the way to the detector, an electromagnetic magnet is put on the way to the detector, deviating the molecules by a certain angle in function of the mass of the molecule.
The kinetic energy Ek of the ions is given by the repulsion of the repeller and the speed v of the ions depends thus on their mass m and their charge z.
V is the difference of potential between the acceleration lenses. To reach the detector, ions pass through the magnet and are deflected by its magnetic field B. Only one trajectory leads to the detector, when the centrifugal force equals the magnetic centripetal force, i.e. when
We can thus determine the ratio m/z of the ions that reach the detector as a function of the applied magnetic field B:
The same process can be repeated with a second magnets, in the case of double focalisation spectrometers.
Quadrupole
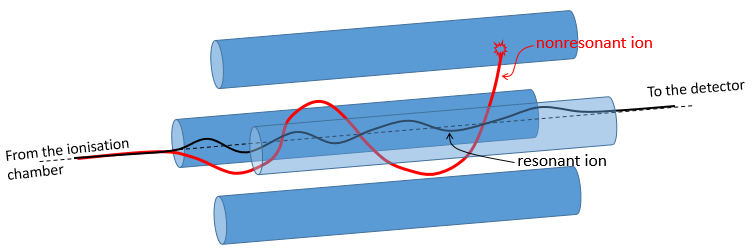
On their way to the detector, the ionised molecules are surrounded by four long parallel electromagnets.
Parallel magnets are set to one given frequency. It allows to control the trajectory of the molecules with one specific mass/charge ratio. Only those species will have a stable path that is parallel to the magnets and reach the detector. The other species are deflected and will eventually collide with one of the magnet where they lose their charge. A range of frequencies is scanned to allow all of the ionised molecules to reach the detector separately.
Ion trap
The principle is similar to the one of the quadrupole except that the ions are maintained in a room between electrodes. They are not moving towards the detector. The ions which are in resonance with the electric field remain trapped. If we increase the tension, the ions of larger mass are stabilised while the trajectory of the lighter ions becomes instable and they hit the electrodes.
Detector
As we detect single ions, the signal has to be magnified several times. It is done by a series of dynodes that increase the signal first obtained on a cathode. The final signal reaches an anode and has been multiplied by 106-7 on its way.
The accuracy of the setup has not to be extremely high and it would actually change almost nothing. The important is that a difference of 1 unit of atomic mass can be detected.